
Teaching Practice
History
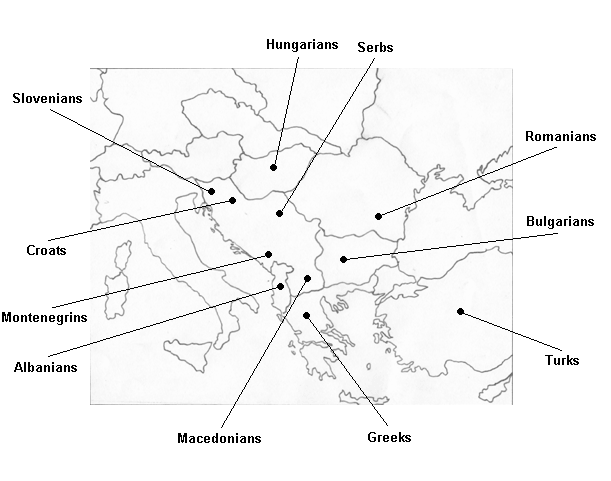
THE VERSAILLES SYSTEM IN SOUTH/EASTERN EUROPE - ESTABLISHING OF NEW ORDER (1919-1925)

|
South-East Europe Textbook Network |
|
Teaching Practice |
Teaching Practice History THE VERSAILLES SYSTEM IN SOUTH/EASTERN EUROPE - ESTABLISHING OF NEW ORDER (1919-1925)
|